Browsers implement CORS to protect users, not servers
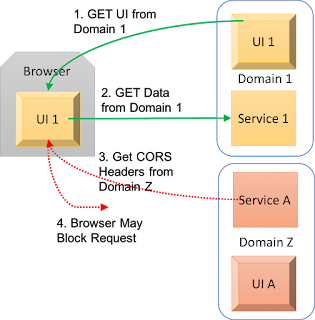
CORS is designed to protect users from cross site attacks where one site has the browser execute code to connect to another site without the user recognizing that it happened. CORS relies on the Web Browser to recognize and block disallowed cross site requests. Server side CORS does not block service requests or protect a web site from direct interrogation and or programmatic attack. Applications and Internet facing services cannot rely on CORS for general site protection. They can rely on CORS to protect the site when the site is connected to by a web browser. Companies should not consider CORS any type of secure Authorization model. They should implement CORS policies that provide least privilege where possible. Specified by Server, Implemented by Browser Application servers can say that they allow connections from any browser no matter where that original browser session / page originally resided. This makes it simple for any page to aggregate in...